Which Of The Following Is Most Concerned With The Design Of New Or Changed Services?

It is an established fact that the ITIL service lifecycle has 5 stages – service strategy , service design , service transition , service operation , and continual service design . All these stages are equally important to help ensure that It services are delivered of the highest quality possible and the customer is kept happy. Nonetheless, among these stages, the service design phase is of more significance than the other stages.
Most organizations tend to skip the service design phase completely. They program their services (service strategy) and so directly become on to implementation (service transition and operation). Service design is ignored as a process in itself. This eventually leads to several agin furnishings,
-
- The customer is not happy with the level of service existence provided.
- Feature modification and enhancement requests postal service-implementation.
- Last-minute fixes to service process and workflow.
- IT staff requiring training to provide better service.
These aspects are not normal characteristics of a successfully delivered service. They only go on to represent a poorly planned service that was implemented without the necessary service pattern in place.
The objective of Service Design
Empathise why ITIL Service Design is almost important for It services. The primary purpose of service blueprint is to plan and design IT services together with the governing IT practices, processes, and policies to realize the service provider's strategy, and to facilitate the introduction of these services into supportive environments ensuring quality service delivery, customer satisfaction, and toll-effective service provision.
There are 4 primal principles upon which service design functions are based upon.
- People (stakeholders)
- Processes
- Products (applied science, tools, services)
- Partners (vendors, manufacturers)
All these principles course the foundation for the v pattern aspects of service pattern.
-
Service Solutions:
All the functional requirements, resources, and capabilities are needed and agreed upon.
-
Service Management Systems and Tools:
To ensure consistency with other services and guarantee that supporting and dependent services are adequate to maintain on-going reliable service delivery.
-
Engineering Architecture and Management Systems:
To ensure they are consistent with the new service and are suitable to operate and maintain information technology.
-
Processes:
To ensure that the process, roles, and responsibilities are adequate to operate, support, and maintain the new or changed service.
-
Measurement Methods and Metrics:
To ensure that the right parameters are set which volition help assess the quality of service provided
All these design elements demand to be documented and tracked to ensure that they are being created for each attribute of a new service or changed service. This certificate is called the Service Blueprint Packet. The service transition phase volition make apply of this service pattern package to begin implementing the service.
The indispensable nature of the service design stage to the service lifecycle lies in the fact that service pattern lays the groundwork on which the service is built and this design blueprint consists of the following elements.

Service Design Pattern
-
Service Catalogue:
The purpose of the Service Catalogue Management procedure is to provide and maintain a single source of consistent data on all operational services and those beingness prepared to be run operationally, and to ensure that information technology is widely available to those in the organization who are authorized to access it.
-
Service Level Management:
The SLM procedure is responsible for agreeing and documenting service level targets and responsibilities within Service Level Agreement (SLA) and Service Level Requirements (SLRs) for every service and related activeness within IT. This process ensures that all current and planned It services are delivered to agreed and achievable targets.
The Operational Level Agreement (OLA) is likewise a role of this process. An OLA is an agreement between an Information technology service provider and another part of the same organization that assists with the provision of services – for instance, a facilities department that maintains the air-conditioning, or a network back up team that supports the network service. -
Capacity and Availability Management:
The purpose of the Capacity Management process is to ensure that the capacity of IT services and the IT infrastructure meets the agreed capacity and performance-related requirements in a cost-effective and timely manner.
Availability on the other hand is the ability of a Configuration Particular or IT Service to perform its agreed function when required. Availability is usually calculated as a percentage. This calculation is oft based on agreed service time and reanimation. It is best exercise to calculate availability using measurements of the business output of the IT service. -
IT Service Continuity Management:
IT Service Continuity Management supports the overall business continuity past ensuring and managing the risks that could seriously impact IT services. The IT service provider can ever provide minimum agreed business continuity related service levels.
-
Information Security Management:
The value of information security tin never exist stressed enough in a service environs. The Information Security Management process aligns It security with business security and ensures that the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the organisation'due south assets, information, data, and It services always match the agreed needs of the business.
-
Supplier Management:
Tertiary-political party suppliers play a key role in the successful delivery of an Information technology service when managed efficiently. The Supplier Direction process obtains value for money from suppliers and provides seamless quality of IT service to the business by ensuring that all contracts and agreements with suppliers support the needs of the concern and that all suppliers meet their contractual commitments.
These 6 processes ensure that the service blueprint covers all bases in terms of the five blueprint aspects. When the design blueprint is solid, information technology provides the perfect start indicate for the operational guys to showtime implementing the service. The value of the service design procedure to an Information technology service can be summed upward in these 4 following benefits.
-
- Comeback of quality and consistency of service
- Ease the implementation of new or changed services
- Improve service alignment with the system's goals
- Reduce total cost of ownership
Design Coordination in ITIL
The final process in the ITIL service blueprint phase of the ITIL Lifecycle for services is the design coordination process. Information technology is a useful part of service design that has been newly added in the revised ITIL V3 edition.
The main purpose of blueprint coordination is to make certain that the objectives of the blueprint stage are fulfilled as per the requirement. It aims to coordinate all the service design activities, processes, and resources.
Objectives of Pattern Coordination in ITIL
The objectives of the design coordination process are:
-
To make plans and organize all the design activities
-
To produce Service Blueprint Packages based on change requests and service charters.
-
To make sure that only the appropriate service designs are produced and transferred to service transition equally previously agreed upon.
-
To validate the uniformity in the establishment of It services, service direction information systems, processes architectures, metrics, and technology.
-
To manage the interfaces with service strategy and service transition
-
To increase the efficiency and efficacy of the activities and processes of service design.
-
To finer manage all the pattern activities across various projects, changes, support teams, and suppliers in addition to supervising resources and schedules.
-
To ensure consistency in the blueprint of the following in society to meet the nowadays and future needs and requirements of businesses that are always evolving:
-
Appropriate services
-
Service management data systems
-
Architectures
-
Engineering science
-
Processes
-
Information
-
Metrics
-
Scope of Pattern Coordination in ITIL
All pattern activity comes under the telescopic of pattern coordination. The scope of the design coordination varies from one organization to some other every bit each company will have unlike objectives, visions, and strategies.
-
Sure design efforts will be a role of a project and others will be managed solely via the change process, without a formally defined project.
-
Design coordination needs to pay maximum attention to major changes.
-
Every organization needs to properly ascertain the level of attention that needs to be applied to each design in design coordination.
-
The interaction betwixt the design and processes, review, measurement, and comeback of service blueprint besides come up nether the telescopic of the pattern coordination process.

Value of Design Coordination in ITIL
The blueprint coordination process makes sure that the desired business organisation outcomes are provided by consistent quality solution designs and service design protocols.
Procedure Activities of Design Coordination in ITIL
The process activities under pattern coordination come under two categories:
-
Activities that are related to the overall service blueprint lifecycle stage.
-
Activities are related to each individual design.
The stages of the process activities are shown in the flowchart beneath.
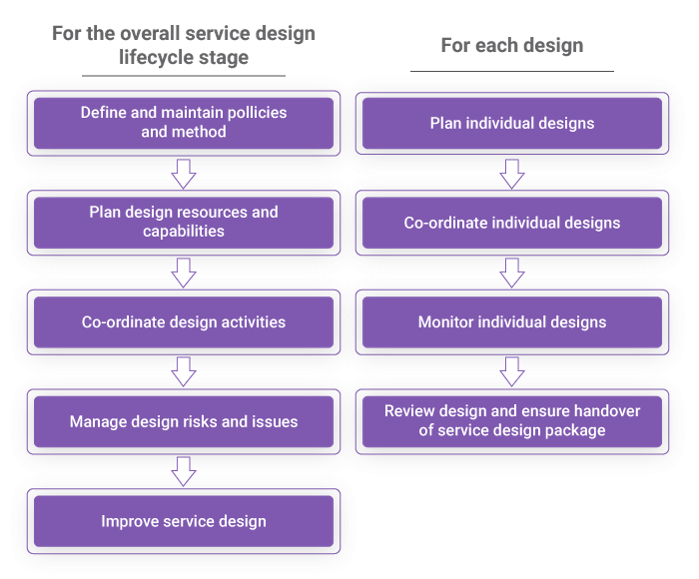
Sub-Processes of the Design Coordination Process
-
Blueprint Coordination Back up
The aim of this procedure is to manage and develop service design resources and competencies in order to make sure that a reliable and steady approach is implemented beyond all the service transition projects.
-
Service Design Planning
The aim of this process is to make detailed plans of all design activities to ensure that all relevant topics are taken into account during service pattern.
-
Service Design Coordination and Monitoring
The aim of this process is to coordinate the blueprint activities which are performed by multiple service pattern processes and to find out if the services which are newly implemented or changed can be provided economically.
-
Technical and Organizational Service Design
The aim of this process is to find out the mode in which a new service will exist provided from an Information technology perspective, by specifying the technical infrastructure which needs to be created along with the organizational changes which are required.
-
Service Blueprint Review and Request for Change Submission
The aim of this procedure is to provide the service pattern package for a concluding review and start the implementation of the service by submitting a formal RFC (Asking for Change).
Challenges of Blueprint Coordination in ITIL
The challenges involved in the design coordination process are:
-
Maintaining high-quality Service Design Packages throughout the complicated landscape consisting of unlike businesses, services, and infrastructure.
-
To ensure that adequate resources are allocated to design coordination activities.
-
To develop mutual practices which produce the high-quality designs which are needed, without bringing in unwanted bureaucracy.
Risks of Pattern Coordination in ITIL
The following risks are encountered while implementing design coordination:
-
A lack of available skill and knowledge
-
An absence of involvement from the business organisation in question
-
Business priorities and requirements that are poorly defined or not clearly mentioned.

Decision
These are the reasons why it is of import to spend time and effort in getting the service design procedure correct. Information technology will ensure that your service implementation happens seamlessly at the optimum costs and the service is delivered in such a way that it meets the expectations of the customer.
Larn more about Service Management all-time practices through Invensis Learning's IT Service Management certification training onITIL 4 Foundation,SIAM Foundation ,SIAM professional,VeriSM, etc.
Source: https://www.invensislearning.com/blog/itil-service-design-and-its-importance/
Posted by: meachamhiscon.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Is Most Concerned With The Design Of New Or Changed Services?"
Post a Comment